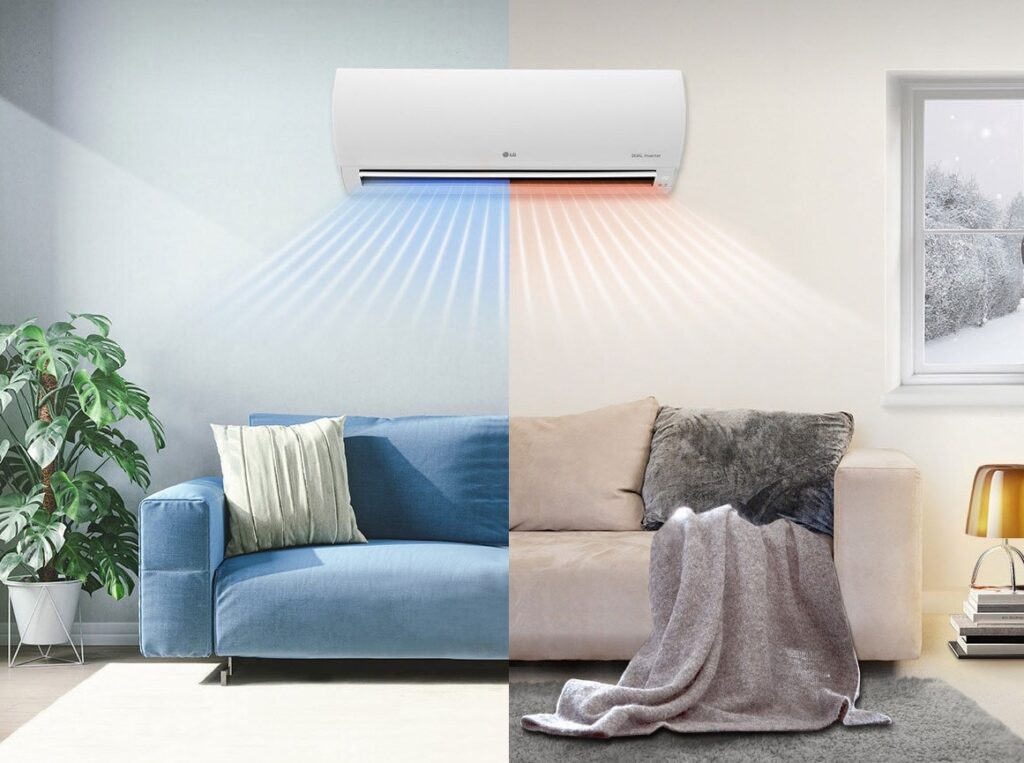
A heat pump is a type of HVAC system that is used to transfer heat from one location to another. Unlike traditional heating and cooling systems that generate heat or cool air, a heat pump moves heat from one area to another. In this blog post, we will discuss how a heat pump works and the different types of heat pumps available.
How a Heat Pump Works
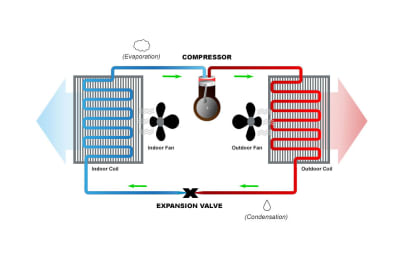
A heat pump works by using a refrigerant to transfer heat from one location to another. The refrigerant circulates through the heat pump’s coils, absorbing heat from the air or ground outside and transferring it to the air inside your home or building. During the summer months, the heat pump operates in reverse, removing heat from the indoor air and transferring it outside.
There are two main components of a heat pump: the indoor unit and the outdoor unit. The indoor unit contains the evaporator coil, which is responsible for absorbing heat from the indoor air. The outdoor unit contains the condenser coil, which releases the absorbed heat outside. The two units are connected by a refrigerant line that circulates the refrigerant between them.
Types of Heat Pumps
There are three main types of heat pumps: air-source heat pumps, ground-source heat pumps, and water-source heat pumps.
Air-Source Heat Pumps
Air-source heat pumps are the most common type of heat pump and are used in many homes and businesses. They work by absorbing heat from the outdoor air and transferring it inside. These heat pumps are most effective in moderate climates, as extreme temperatures can cause them to become less efficient.
Ground-Source Heat Pumps
Ground-source heat pumps, also known as geothermal heat pumps, work by absorbing heat from the ground and transferring it inside. These heat pumps are more efficient than air-source heat pumps because the temperature of the ground remains relatively constant throughout the year. However, they are more expensive to install because they require a ground loop system to be installed underground.
Water-Source Heat Pumps
Water-source heat pumps work by absorbing heat from a nearby water source, such as a lake or river, and transferring it inside. These heat pumps are most commonly used in commercial buildings near bodies of water.
Benefits of Using a Heat Pump
There are several benefits to using a heat pump for heating and cooling. These benefits include:
- Energy efficiency: Heat pumps are more energy-efficient than traditional heating and cooling systems because they move heat rather than generate it.
- Cost-effectiveness: Heat pumps can save you money on your energy bills, as they use less energy to heat and cool your home or building.
- Environmental friendliness: Heat pumps are a more environmentally friendly option for heating and cooling because they produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions than traditional systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a heat pump is a type of HVAC system that transfers heat from one location to another. There are three main types of heat pumps: air-source heat pumps, ground-source heat pumps, and water-source heat pumps. Heat pumps are a more energy-efficient and cost-effective option for heating and cooling, and they are also more environmentally friendly. If you are interested in installing a heat pump in your home or building, be sure to consult with a licensed HVAC contractor to determine which type of heat pump is best for your needs.